#kathrein #lyrasa #kathreincables #caoxialcables #screeningattenuation #returnloss
Coaxial Cables And The Meaning Of Screening Class. KATHREIN New Optimized Series of Coaxial Cables.
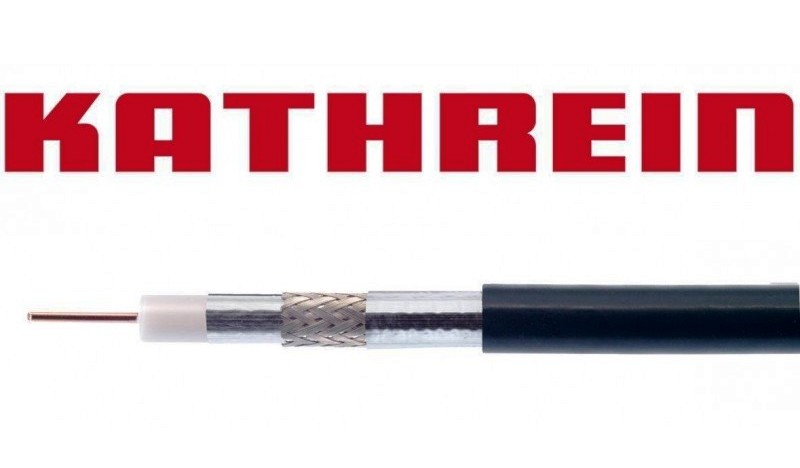
Coaxial Cables: LCD 111 A ++ & LCD 115 A ++
Features:
Impedance: 75 Ohm metre marking- Conforms to: EN 50117 / screening class A + - Approved by KDG/Vodafone Kabel Deutschland
Material certified by dibkom
- LCD 111 A+
Screening attenuation typ. 130 dB
Building product regulation EU 305/2011 (EN 50575) Fire classification: Eca
Lead free, silicone free, UV-resistant
Available in 100 m, 250 m and 500 m lengths
Suitable for home installation and exterior applications (no grounding)
Suitable connectors EMK 01, EMK 02 threaded; EMK 11 Crimp; EMK 12 compression; EMK 20 self install
Suitable IEC connectors: compression male EMK 63; compression female EMK 64; threaded male EMK 21; threaded female EMK 62
- LCD 115A+
- Screening attenuation typ. 130 dB
- Building product regulation 305/2011 EN 50575 Fire classification: Cca s1a,d1,a1
- Halogen-free, lead-free, silicone free and UV-resistant
- Suitable for home installation and exterior applications (no grounding)
- Available in 100 m and 500 m lengths
- Suitable F-type connectors EMK 01 & EMK 02 threaded; EMK 11 Crimp; EMK 12 compression; EMK 20 self install
- Suitable IEC connectors: compression male EMK 63; compression female EMK 64; threaded male EMK 21; threaded female EMK 62
The Meaning Of Screening Class
Any coaxial cable carrying a TV signal also acts as a receiving antenna because it receives external electromagnetic signals which it adds to the signal it carries. At the same time, it also acts as an emitting antenna, emitting in the surrounding space a portion of the signal it carries.
The shield defines and defines the resistance of the coaxial cable to external electromagnetic interference.
At the frequencies of 5-30 MHz, the shielding measure is the transfer impedance (Zt) at mOhm / m. The smaller the Zt value in mOhm / m, the better armored the cable.
At frequencies of 30-3000 MHz, it is expressed as screening attenuation (As) in dB. The higher the value of As in dB, the more the cable manages to attenuate the interference, so it better "protects" the signal it carries. Also, the better the shielding, the less the percentage of the signal carrying the cable is emitted into the environment.
The sources of interference
Nowadays the shielding of cables is of particular importance because:
There are a lot more electromagnetic signals in the atmosphere from the past and therefore more potential sources of interference: Microwave ovens, thermostats, lighting switches and dimmers, other neighboring cables, mobile and cordless phones, wireless internet routers, radio-controlled games, computers, netbooks, electronic games, baby monitors, video senders, wireless speakers, etc.
Therefore, a very important parameter for a cable is its shielding, especially in today's era where electromagnetic signals within homes, offices, hospitals, hotels, and generally all buildings, but also in the atmosphere, their sources of origin and their power, are constantly increasing.
Simple cables with 60 or 70 db shields are often interfering with various broadcast sources, such as the 950-2250 MHz frequencies used by mobile phones. When a cable carries digital signals (eg satellite or terrestrial digital reception) , interference may result, for example, to "freeze" the image, and to a number of other problems.
Often the shielding is confused with the optical coat of the coaxial cable outer grid. This is not correct. The high overlap is not in itself sufficient to ensure high shielding. There are a number of other construction parameters that each contributes to the final result, which ultimately results only with specialized measurements. In addition, to determine the shielding class, measurements of both Zt & As parameters are required.
Highly shielded cables are the best choice for carrying digital signals.
The EN 50117 series of standards classifies coaxial cables in classes based on their shielding.
Today in Europe and Not only, shielding is the primary feature of selecting a coaxial cable and there is a clear trend towards the use of A + and A ++ cables.
All KATHREIN wires meet, comply and are certified according to:
According to: EN 50117 Class A + EN: 50117-2-3 of 2004 + A1 of 2008 + A2 of 2013 EN: 50117-2-4 of 2004 + A1 of 2008 + A2 of 2013 Low Voltage Directive 2006/95 / EC of 12/12/2006 EN: 60728-11 of 2005 2010 RoHS 2011/65 / EU from 08/06/2011 EN: 50581 of 2012
Fire safety regulations for coaxial cables: ΕΝ: 50575 Ε.Ε. No 305/2011 in force since 01 July 2017. EN: 50575 of 2014 + A1 of 2016 Approved by KDG / Vodafone Kabel Deutschland Certified material by dibkon
The development, production, quality assurance and marketing are based on EN: ISO 9001 (All CE Certificates and Fire Safety Certificates are available). The quality of the outdoor enclosure depends on the time that the cable will withstand severe and extreme weather events (floods, heavy rainfall and snowfall, humidity, sudden temperature fluctuations, heatwaves) on ultraviolet radiation, if placed in the ground or in fresh water or even underwater.
A poor quality enclosure will allow moisture to penetrate the first few meters, and although the other elements of the cable (bleed, aluminum, etc.) are of poor quality, they will soon erode all of them, leading to an increase in their losses and then the cable stops completely signaling. It is advisable, where possible, to place the cable in channels or to select protected waypoints so that its life spans. When its losses increase over time and begin to show signs of deterioration or increased losses, it should be replaced. Another quality parameter in cables is rodent resistance and also non-flammable.